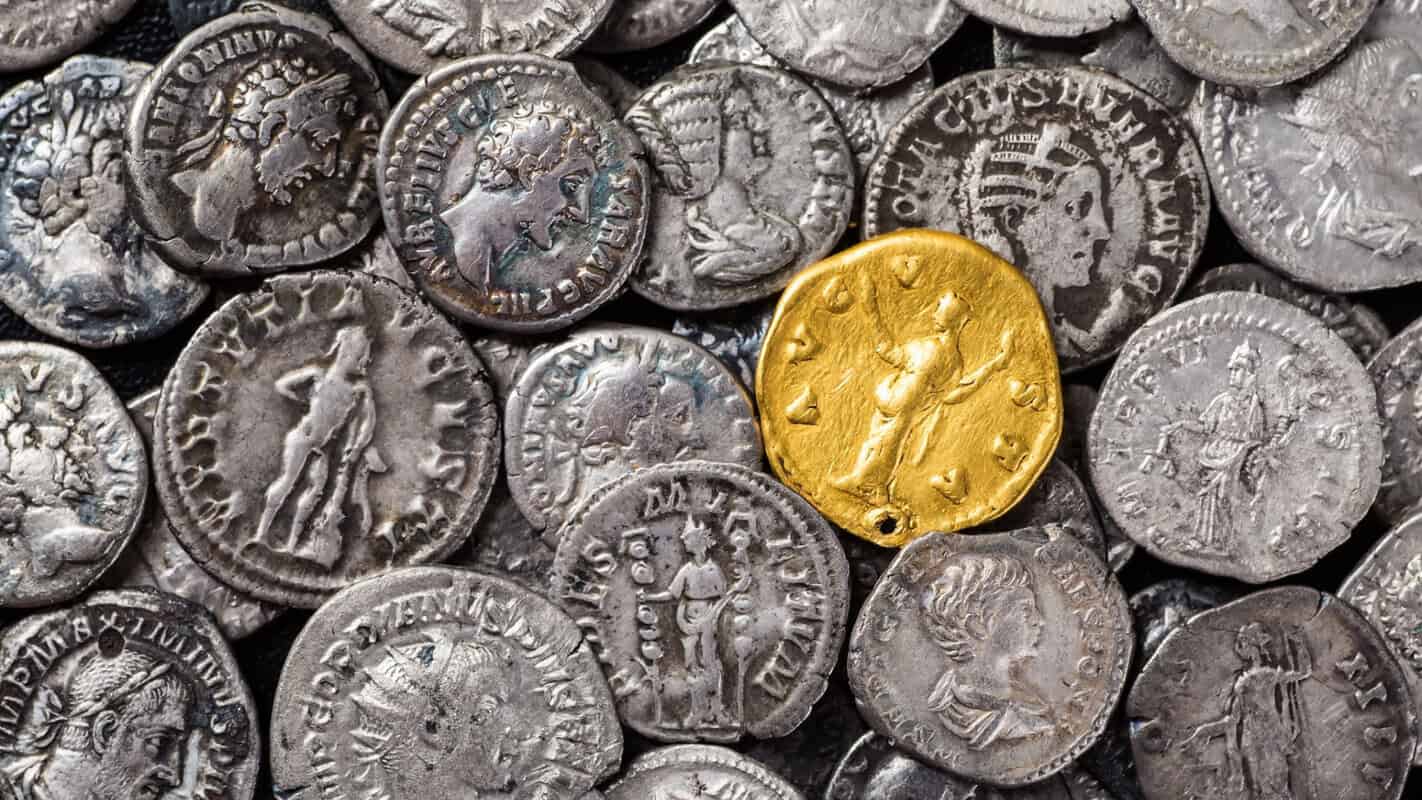
When we think of ancient Rome, we imagine grand architecture, mighty armies, and legendary emperors. But one of the most tangible connections to that era fits easily in the palm of your hand: Roman coins. At BidCurios, where collectibles meet passionate collectors, Roman coins hold a special place—not just as investments, but as direct artifacts of history.
The Origins of Roman Coinage
Roman coinage began around 300 BCE, as Rome grew from a regional power into a global empire. Early Roman money was simple—bronze lumps known as aes rude. Over time, the system evolved to include cast bronze coins (aes grave), and eventually struck silver and gold coins that mirrored Rome’s expanding ambitions.
The first true Roman silver coin, the denarius, emerged around 211 BCE during the Second Punic War. It quickly became the backbone of Roman commerce, used from Britain to Egypt. Coins weren’t just economic tools; they were propaganda, spreading the image and power of Rome’s leaders far and wide.
Coins as Tools of Power and Propaganda
Roman coins often featured portraits of emperors, gods, and symbols of Roman authority. Julius Caesar famously placed his own image on coins during his lifetime—a bold move that reinforced his dominance and changed coinage forever. After him, every emperor used coins to project legitimacy, victories, and divine favor.
Inscriptions on coins—usually in Latin—celebrated achievements, military conquests, or divine ancestry. A coin minted under Emperor Augustus might proclaim “DIVI F” (Son of the Divine), linking him to the deified Julius Caesar. Coins were Rome’s mass media. In a world without newspapers, a coin in your hand carried the news of empire.
Why Collect Roman Coins Today?
Every Roman coin is a survivor. Many circulated for decades or even centuries before being lost or buried. When you hold one today, you’re not just collecting metal; you’re touching an object that passed through ancient markets, into the pockets of merchants, soldiers, and citizens.
Collectors value Roman coins for their artistry, historical importance, and variety. From the humble bronze as to the gold aureus struck for emperors, there is something for every level of collector. Plus, each coin comes with its own mysteries—whose hands held it, and what moments of history did it witness?
Start Your Journey into Roman History
At BidCurios.com, we offer a curated selection of authentic Roman coins, each verified and sourced for collectors who want more than just a collectible—they want a connection to the past. Whether you are new to ancient coins or expanding an existing collection, Roman coins offer a rich and rewarding journey.
Explore our collection today and hold a piece of history.
👉 Browse Roman Coins on BidCurios.com
Ancient Roman Coins

Ancient Roman Coin King Gallienus Antoninianus 253-268 AD, 1.5 grams
₹2,999.00

Ancient Roman Coin Maximinus II Follis, 310-313 AD, 7.5 grams
₹7,999.00

Ancient Roman Coin King Gallienus Antoninianus 253-268 AD, 2 grams
₹2,999.00